Understanding and Treating Gum Disease
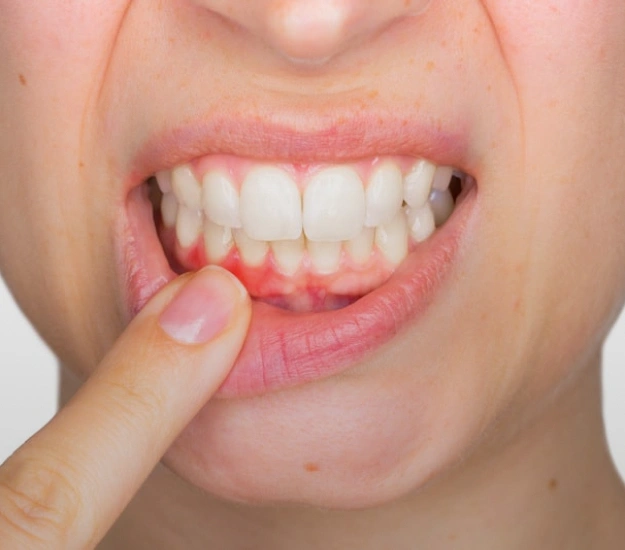

Gum disease is one of the most common oral health issues in America. It has been estimated by the CDC that about half of all American adults suffer from some form of gum disease. Proper at-home care and intervention from a dentist are critical for preventing gum disease from progressing and keeping your teeth and gums healthy.
For most people, the first sign of gum disease is bleeding gums. This can be a sign that you have gingivitis – the initial, mild form of gum disease, in which your gums are infected with bacteria. You shouldn’t worry about this unduly, but you should make an appointment with your dentist, because left untreated gingivitis can become more serious.
Specifically, if you leave gum disease untreated, it can become periodontitis. In this stage of the disease, the infection can cause permanent damage to the structures of the teeth and gums. Both gingivitis and periodontitis have been shown to raise your risk of more serious diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, osteoporosis, pneumonia, and cancer.
- Bad breath, caused by the bacterial infections
- Receding gums, as your gums pull away from the site of infection
- It hurts when you floss
- It hurts when you brush
- Your gums bleed when you brush or floss
- You notice your gums are very red
- You notice your gums are puffy and sensitive
- Sensitive teeth, or teeth that feel loose

